Bioinformatics and the Pharmaceutical Industry
- 25th October 2021
- Posted by: Breige McBride
- Category: Bioinformatics

The pharmaceutical industry uses bioinformatics throughout the drug discovery and development process. In this blog we’ll take a closer look at the particular analyses that are beneficial at each stage, starting with the preclinical phase then moving into clinical development.
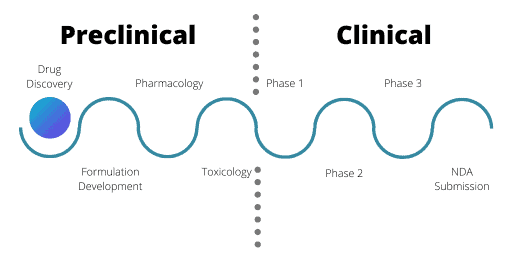 Stages of the Drug Discovery and Development Process
Stages of the Drug Discovery and Development Process
Bioinformatics in Pharmaceutical Development: Preclinical Stage
Using bioinformatics in the preclinical stage of drug development improves lead selection quality, speeds up target validation, enhances mechanistic insight, and delivers predictive safety modelling. All of these factors help to lower costs and save time, while improving the likelihood of success in preclinical development and beyond.
Identifying Drug Targets and Leads
The overall purpose of pharmaceutical companies is to create new drugs to treat diseases and other medical conditions. This process begins with identifying a drug target. This is a molecule in the body (such as a protein or gene) that is associated with the disease to be treated. Pharmaceutical companies also need to develop a chemical compound that has the potential to treat the disease. Researchers refer to this as a drug lead until they know it is safe to use and successful at treating the disease.
How Bioinformatics Helps the Pharmaceutical Industry Identify Drug Targets and Leads
Bioinformatics approaches help identify drug targets and leads in a variety of ways. For example, analyses of the data generated from High-Throughput Screens (HTS) can be used to identify a drug lead. Similarly, analyses of data from preclinical experiments using animal models, diseased human tissues and cell lines can identify drug targets as well as leads.
Validation of Drug Targets and Leads
Once they have been identified, drug targets and leads then need to be validated. To achieve this. researchers must demonstrate that the drug lead affects the target molecule in a way that provides a positive therapeutic outcome.
Using Bioinformatics to Validate Drug Targets and Leads
Target validation can be supported by robust analyses of CRISPR screen data or gene expression data generated from models in which the target has been knocked-out or knocked down.
Whereas lead validation can be established by comparing gene expression data from untreated models and models treated with the identified lead. This comparison gives insights into the lead mode of action.
Additionally, both drug target validation and drug lead validation can be supported by in silico comparisons of preclinical results with publicly available data.
Bioinformatics in Pharmaceutical Development: Clinical Stage
The clinical stage in drug development is when researchers administer the drug to human volunteers in clinical trials. There are 3 phases of clinical trials and each has a different aim. The primary aim of Phase 1 trials is to test the safety of a drug in healthy volunteers. Phase 1 trials also assess what dose of the drug the human body can tolerate and may assess an element of drug efficacy.
Following Phase 1, Phase 2 trials then test the drug in the relevant patient population (exceptions are oncology drugs and orphan disease therapeutics). Often there are 2 parts of Phase 2 trials; Phase 2a and Phase 2b. In these cases, Phase 2a trials test a smaller number of patients. It is common for multiple Phase 2 trials to run simultaneously, testing various clinical indications, combinations, or formulations of the drug.
Finally, there are Phase 3 trials. In these trials, researchers compare the trial drug to current drugs already available to treat the same condition. To pass a Phase 3 trial the trial drug must be better than the current drugs available. For example, the new drug must be more effective or have less side effects. Similarly to the preclinical phase, bioinformatics plays a key role during the clinical stage via the analysis of the vast datasets being produced. You will find more detail about this below.
How Bioinformatics Benefits the Pharmaceutical Industry at the Clinical Stage
Phase 1, 2, and 3 trials all generate data, often in vast amounts. As a result, bioinformatics has become essential. Bioinformatics analyses can be applied to data from primary outcomes as well as each of the following data types which can be generated during clinical trials:
- Genotype Data
- Demographic Data
- Gene Expression Data
- Clinical Phenotypes
- Clinical Chemistry
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Flow Cytometry
- Haematological tests
- Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing
- Cytokine profiling
- Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic measurements
Applying bioinformatics approaches to clinical trial data ensures we reveal all of the key insights in the data. In turn, these insights can then inform the next steps and ensure maximum return on investment in pharmaceutical research.
What’s more, we can use bioinformatics approaches to integrate multiple data types. In fact, almost all types of biological data can be integrated together for analysis. For example, in preclinical development we can combine gene expression changes with copy number variant (CNV) and mutational data to identify biomarkers that are indicative of a compound’s sensitivity. Meanwhile, in clinical development, we can integrate different data types to help assess safety, tolerability, and efficacy for patients. For example, we can combine proteomics data with pharmacokinetics (PK) data to assess patient outcomes after treatment and relate response to exposure.
Drug Repurposing
In addition to supporting drug development, bioinformatics providers can also support the pharmaceutical industry when it comes to drug repurposing. Bioinformatics services can help repurpose drugs via:
- Signature generation of compound effects
- In silico assessment of potential indications for repurposing using on- and off-target effects
- Data landscaping and mining for markers in potential indications of interest
Ultimately, these services help pharmaceutical companies to maximise the value of their drug pipelines by repurposing or repositioning their drug or novel therapeutic for new indications.
Summary
As explained above, bioinformatics is an essential tool in the pharmaceutical industry’s toolbox. Bioinformatics analyses provide key information throughout the entire drug discovery and development process, from aiding the identification and validation of drug targets and leads through to helping assess the outcomes of phase 1, 2 and 3 clinical trials; as well as supporting drug repurposing efforts.
In fact, pharmaceutical companies regularly rely on Fios Genomics’ bioinformatics services to get the most out of their research data. Some pharmaceutical companies we have worked with include Pfizer, GSK, Unilever, Roche and Merck, to name a few. If you would like to learn how we can support your drug discovery or development project with bioinformatics, you can use the form below to contact us. We will be happy to discuss your goals, give advice on the most suitable bioinformatics analyses to help you achieve them, and provide a quote if required.
Ask Fios Genomics
Want to discuss your project, ask a question or request a quote? Use this form to submit your enquiry and a member of our team will get back to you!
Alternatively, you can browse our bioinformatics services or learn more about what it is like working with Fios Genomics on our clients and partners page.
We hope you found this information useful, thanks for visiting our blog!
Author: Breige McBride, Content and Social Media Manager, Fios Genomics
Reviewed by Fios Genomics Bioinformatics Experts to ensure accuracy
Case Study Examples:
Pharmacological Inhibition of PMS2
Transcriptome Analysis of Antigen-Specific T‑Cell Responses
See Also:
How Fios Genomics can advance preclinical research
How Fios Genomics can advance clinical research
What are the benefits of drug repurposing ?
What is the drug development process?
How ‘omics analysis can better inform precision medicine strategies prior to clinical trials
How to reduce the drug development timeline
Using Biobank Data to Reach Your Research Goals
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.