Bioinformatics Reveals Secrets of Gut Microbiome
- 19th April 2023
- Posted by: Breige McBride
- Category: Microbiome
The gut microbiome holds many secrets which researchers are revealing bit by bit, study after study. This blog details some of the latest research showing different ways gut microbiota impact overall health. We also explain how microbiologists and other researchers can leverage bioinformatics analyses to further their gut microbiome research to reveal even more of its secrets. However, it is important to cover the basics first, so let’s define what the gut microbiome actually is.
What is the gut microbiome?
A microbiome is the collection of genomes from all the microorganisms found in a particular environment. So, the gut microbiome refers to all the genomes of all the microorganisms, such as bacteria, archaea and eukarya, found in the gut.
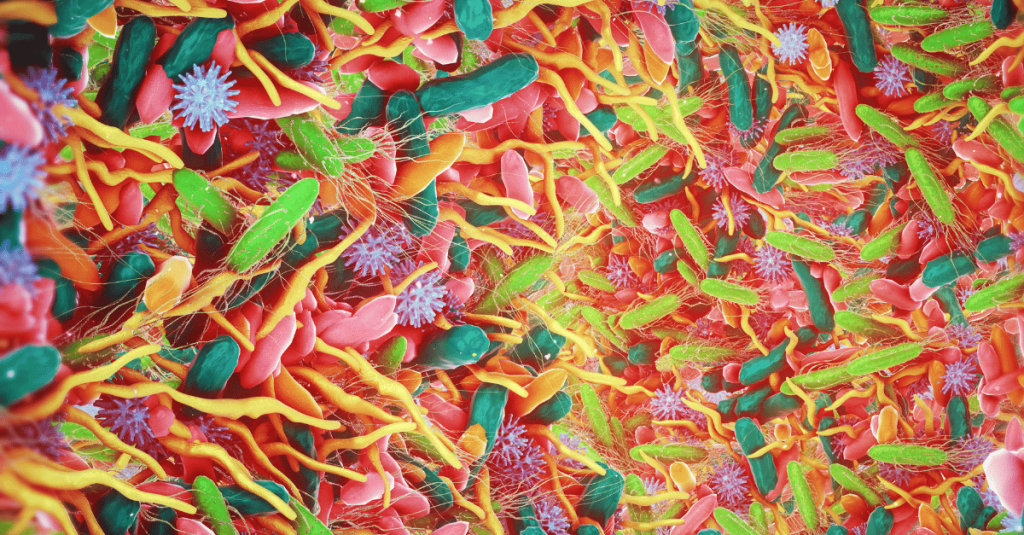
Where is it?
Although ‘gut’ refers to both the small and large intestines, the majority of microorganisms within the gut are in the large intestine, within the colon 1.
Why is it important?
The gut microbiome is important because it influences an individual’s health. For example, in humans, the microbiota in our gut can impact the symptoms of neurological disorders 2, play a role in the development of chronic inflammatory conditions such as asthma 3 and impact how effective some medical treatments are 4. In fact, our gut microbiomes may even impact our mental health 5 as well as how long we live 6.
How long does it take to alter the gut microbiome?
Humans can alter their gut microbiome very quickly, with the process beginning in a matter of hours, by making changes to their diet. For example, changing from a high-fat to low-fat diet, or from a plant-based to a meat-based diet, can significantly alter not only the levels of different bacteria in the gut, but also the genes those bacteria express 7. What’s more, simply changing how some foods are prepared for consumption i.e. eating cooked vegetables instead of raw vegetables, can also change gut microbial composition 8.
Using Bioinformatics to reveal the gut microbiome’s secrets
In recent years, researchers have shown how the composition of microorganisms in our gut influences our health, behaviour, and longevity. It is therefore unsurprising that the gut microbiome is now a popular research focus. With its influence on our health being so significant, it is important that we learn everything we can about what is going on in our guts and how this impacts our well-being. Fortunately, bioinformatics can help us to do this by uncovering new insights about the microbiota in the gut. For example, we can use bioinformatics analysis of 16s rRNA sequencing data to quantify the differences in the gut microbiomes of distinct groups, as we have done in our sample gut microbiome analysis report: The role of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of Celiac Disease. You can access this sample report by completing the form at the top of this page, on the right.
To learn more about how bioinformatics can further gut microbiome research, visit our Bioinformatics Solutions for Gastrointestinal Research page, or contact us today to discuss your particular research project and how we can support it with bioinformatics analyses.
Author: Breige McBride, Content and Social Media Manager, Fios Genomics
Reviewed by Fios Genomics Bioinformatics Experts to ensure accuracy
Sources
See Also:
Genetic Variation Analysis: What Can We Learn?
The Future of Bioinformatics in 2023
The Clinical Trial Diversity Problem
Access our Bioinformatics Analysis Reports
Fill in the form below to access the data analysis report our team created. Here, the analysis of 16S rRNA sequencing data helped to compare the microbiomes of celiac disease patients (CeD) to those of first-degree relatives of celiac patients (FDR)
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.