Data Stages in Bioinformatics
- 21st December 2023
- Posted by: Breige McBride
- Category: Bioinformatics
In bioinformatics, data undergo various stages before analysis. This blog explains each of these stages as well as when they occur, using sequencing data as an example. So, if you are not sure of the difference between standardised data and processed data, or the steps between raw data and analysed data, read on!
Data Stages
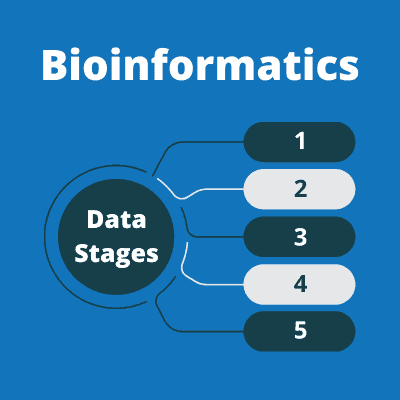
Raw Data
The first stage of data is raw data. This is the unprocessed data gathered directly from sequencing machines (for example). In this stage, the data often contains errors and/or noise.
Processed Data
To get processed data, transformations, and computations are applied to the raw data. This stage includes assembly (in genome sequencing) alignment (in all sequence data), quantification (i.e. measuring gene expression levels), annotation (assigning biological information to sequences), and more. The overall goal at this stage is to extract meaningful biological information from the raw data, with the end product being processed data.
Filtered Data
Filtered data is the third data stage in bioinformatics. Filtering data involves cleaning the processed data of noise, errors, and other unwanted elements. As well as filtering out irrelevant information, this stage includes quality control and the removal of low-quality reads or sequences.
Standardised Data
Once filtered, data may need to be standardised for compatibility and consistency. This is when normalisation happens, enabling data to be transformed or adjusted to a common scale or format. For example, in gene expression studies, normalisation may involve adjusting data to account for differences in data generation platforms or experimental conditions. Once data has been normalised, it may be referred to as standardised data or normalised data. It is important that the correct normalisation method is applied or downstream analysis may be inaccurate.
Analysed Data – The Final Data Stage
Analysed data is the final stage of data in a bioinformatics pipeline. To get analysed data, standardised data is analysed using computational, statistical or machine learning techniques in order to reveal insights or draw conclusions. This may involve comparing datasets, applying algorithms and identifying patterns. It also includes performing differential expression analysis, clustering, classification, and other analytical methods tailored to the biological question being investigated.
If you would like to know what analysed data looks like, you can view one of our sample reports. Simply use the form at the bottom of this page to request a sample report relevant to your research area.
Hopefully, you now have a better understanding of each of the data stages referred to throughout bioinformatics projects. If you have data that requires bioinformatics analysis, we can help. Our bioinformatics experts are always happy to advise on the most suitable analyses to reveal insights from your data that will further your research. Contact us now or view our bioinformatics services for more information.
Request our Sample Reports
Author: Breige McBride, Content and Social Media Manager, Fios Genomics
Reviewed by Fios Genomics Bioinformatics Experts to ensure accuracy
See Also:
Overcoming Objections to Bioinformatics Outsourcing
Examples of Biomarkers and Biomarker Data Analysis